Difference between revisions of "Quantum Control"
m |
|||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
We demonstrate the advantage of applying coherent control technique to 2D-FTES spectroscopy. By shaping individual pulses used in 2D-FTES on atomic model system, we selectively turn on and off specific couplings. This advanced 2D-FTES technique may be useful for probing time-dependent coupling paths among multilevel electronic energy states in complex systems | We demonstrate the advantage of applying coherent control technique to 2D-FTES spectroscopy. By shaping individual pulses used in 2D-FTES on atomic model system, we selectively turn on and off specific couplings. This advanced 2D-FTES technique may be useful for probing time-dependent coupling paths among multilevel electronic energy states in complex systems | ||
| + | Jongseok Lim, Han-gyeol Lee, Jae-uk Kim, Sangkyung Lee, and Jaewook Ahn, "Coherent transients mimicked by two-photon coherent control of three-level system," Phys. Rev. A, 83, 053429 (May 2011). [[Media:LimPRA2011.pdff]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
<br><br><br><br> | <br><br><br><br> | ||
Revision as of 04:59, 17 June 2011
Two photon absorption in strong field
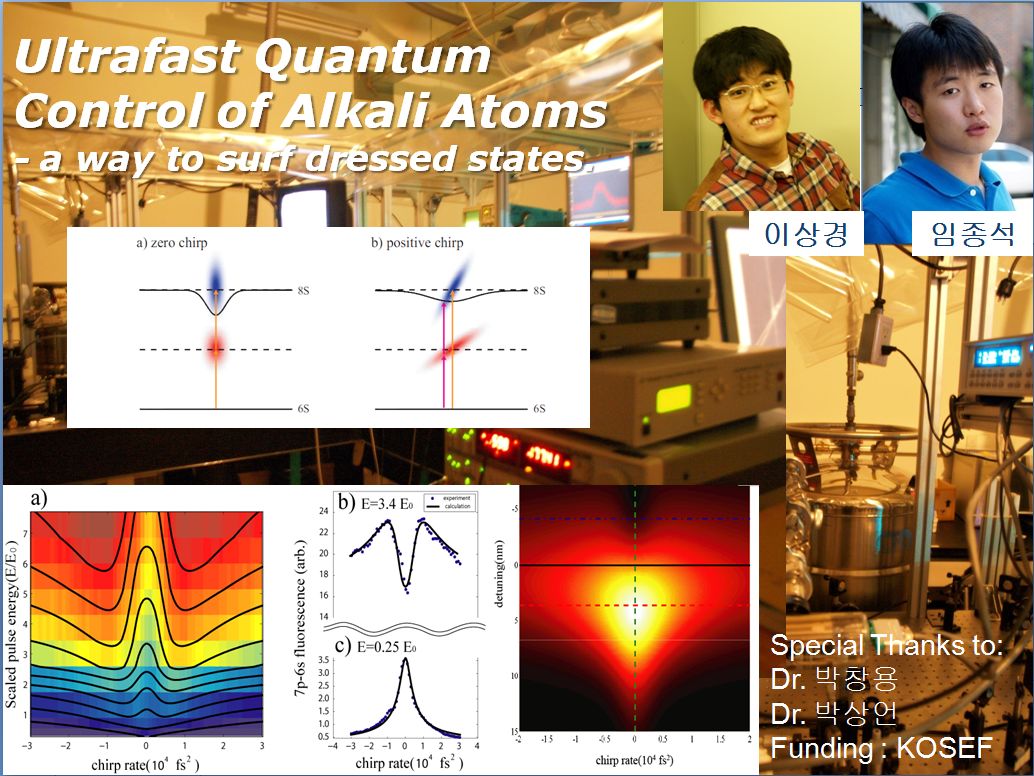
A shaped ultrafast pulse makes it possible to steer a quantum system and thus control a quantum process via light-matter interaction. Two photon absorption (TPA) process in two-level atoms is one of the good testbed for coherent control. We study coherent control schemes for a TPA process in a strong field. For a optimal coherent scheme to enhance TPA, strong field effects (dynamic Stark shift) have been considered.
Strong-field two-photon absorption in atomic cesium: an analytical control approach
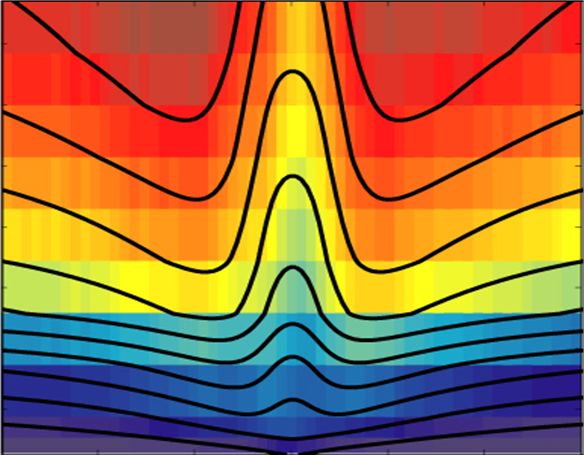
We have considered an analytical control of two-photon absorption process of atoms in the strong-field interaction regime. The experiment was performed on gaseous cesium atoms strongly interacting with a shaped laser-pulse from a femtosecond laser amplifier and a programmable pulse-shaper. When this shaped laser-pulse transfers the atomic population from the 6s ground state to the 8s excited state, we have found that both positively- and negatively-chirped laser pulses, compared with a Gaussian pulse, enhance this excitation in the strong-field regime of laser-atom interaction. This unusual phenomena is explained because the temporal shape of the laser intensity compensates the effect of dynamic Stark shift for the two-photon resonant condition to be optimally maintained. We provide analytic calculations using the strong-field phase matching, which show good agreement with the experiment. 27 April 2009 / Vol. 17, No. 9 / OPTICS EXPRESS 7648
Strong-Field two-photon transition by phase shaping
We demonstrate the ultrafast coherent control of a non-linear two-photon absorption in a dy- namically shifted energy level structure. We use a spectro-temporal laser pulse shaping that is programmed to preserve the resonant absorption condition during the intense laser ¯eld interaction. Experiments carried out in the strong-¯eld regime of two-photon absorption in the ground state of atomic Cesium reveal that the analytically obtained o®set and curvature of a laser spectrum compensate the effect of both static and dynamic energy shifts of the given light-atom interaction. Sangkyung Lee, Jongseok Lim, Jaewook Ahn, Vahe Hakobyan, and Stephane Guerin, "Strong-field two-level two-photon transition by phase shaping," Physical Review A 82, 023408 (August 2010). Media:SangkyungPRA2010.pdf
Coherent Control in 2D-FTES
We demonstrate the advantage of applying coherent control technique to 2D-FTES spectroscopy. By shaping individual pulses used in 2D-FTES on atomic model system, we selectively turn on and off specific couplings. This advanced 2D-FTES technique may be useful for probing time-dependent coupling paths among multilevel electronic energy states in complex systems Jongseok Lim, Han-gyeol Lee, Jae-uk Kim, Sangkyung Lee, and Jaewook Ahn, "Coherent transients mimicked by two-photon coherent control of three-level system," Phys. Rev. A, 83, 053429 (May 2011). Media:LimPRA2011.pdff