Difference between revisions of "Terahertz Optics"
From KAIST Quantum Computing Lab Wiki
Jump to navigationJump to searchm |
m |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
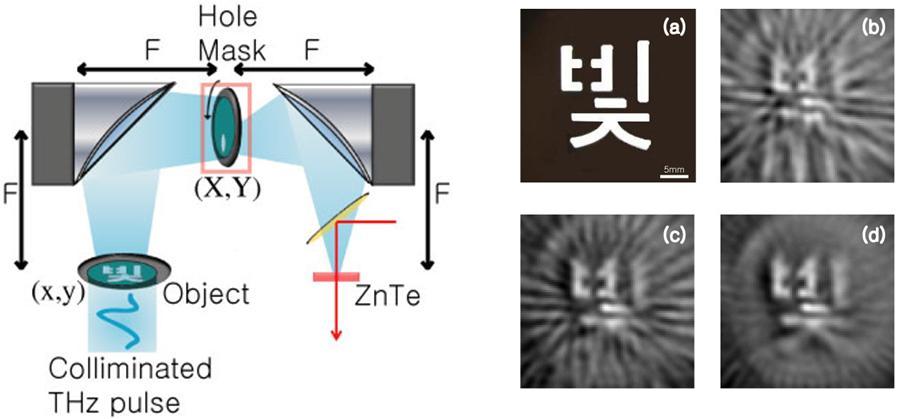
Single point terahertz imagery of 2D objects is demonstrated by exploiting the broadband nature of ultrafast terahertz wave in a coherent optical computing setup. In the devised imagery, a collimated terahertz beam is illuminated on an object and the scattered fields are measured through a spatial mask at the Fourier plane in a 4-f terahertz time-domain spectroscope. This arrangement allows conversion of radial spatial frequencies of the object to the temporal spectrum of the pulse. Hence, a 2D image stored in the terahertz waveforms can be readily obtained. | Single point terahertz imagery of 2D objects is demonstrated by exploiting the broadband nature of ultrafast terahertz wave in a coherent optical computing setup. In the devised imagery, a collimated terahertz beam is illuminated on an object and the scattered fields are measured through a spatial mask at the Fourier plane in a 4-f terahertz time-domain spectroscope. This arrangement allows conversion of radial spatial frequencies of the object to the temporal spectrum of the pulse. Hence, a 2D image stored in the terahertz waveforms can be readily obtained. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Other Activities | Other Activities | ||
Revision as of 00:41, 18 March 2010
THz coherent optical computer
Single point terahertz imagery of 2D objects is demonstrated by exploiting the broadband nature of ultrafast terahertz wave in a coherent optical computing setup. In the devised imagery, a collimated terahertz beam is illuminated on an object and the scattered fields are measured through a spatial mask at the Fourier plane in a 4-f terahertz time-domain spectroscope. This arrangement allows conversion of radial spatial frequencies of the object to the temporal spectrum of the pulse. Hence, a 2D image stored in the terahertz waveforms can be readily obtained.
Other Activities