Difference between revisions of "Korean version"
(→개요) |
m (→개요) |
||
| (9 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==개요== | ==개요== | ||
| − | + | 본 실험실은, 초고속 레이저 기술을 이용하여, 다양한 양자계의 결맞음성, 중첩성, 및 얽힌성을 생성, 변조, 및 측정하는 연구를 수행합니다. 이를 위하여, 알칼리 원자, 분자, 반도체 나노 구조 및 고체 양자계 등의 양자 상태를 분광, 제어, 및 이미징하는 다양한 초고속 광학 기술을 개발하고 있으며, 특히, 펨토초 광학 및 테라헤르쯔파를 이용한 알고리듬형 양자 상태의 제어, 즉 초고속 양자 컴퓨팅의 구현을 목표로 하고 있습니다. | |
| − | + | (1) 양자 결맞음 분광학 : 최근 개발된 결맞음 제어 분광 기술을 통하여, 빛과 다양한 양자계의 상호작용을, 고전적인 한계 이상의 양자 효율로, 양자역학적으로 제어합니다. 2준위 원자 및, 3준위 사다리형 및 V형 원자의 해석적 양자 제어법을 개발하였으며, 다차원 푸리어 분광 양자 제어 기술을 개발을 통하여 양자 논리 소자를 구현하고 있습니다. | |
| − | + | (2) THz 광학 기술 : THz파는 피코초의 짧은 결맞음성을 갖는 양자계를 전기적으로 제어할수 있는 21세기의 새로운 광원이며, 광원 개발, 기초 광학 현상 및 물질의 반응 규명 등 다양한 연구분야가 활발히 연구되고 있습니다. 본 실험실은, 극한적 THz파 물리 현상, 예를 들어, THz 나노분광 및 비선형 분광법을 연구하고 있으며, 궁극적으로는 THz파 양자 제어를 목표로 합니다. | |
| − | + | (3) 새로운 양자계 : 차세대의 양자 제어 분광 대상으로, 다양한 새로운 양자계에 대한 탐사적 연구를 진행하고 있으며, 분자, 반도체 나노 구조 및 강상전자계의 초고속 현상을 연구합니다. | |
| − | + | ==양자 제어== | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[Image:Setup dazzler.jpg|center|400px]] | |
| − | + | 초고속 레이져 펄스는 재단됨에 따라 양자 시스템에 다른 영향을 주며 따라서 빛과 물질의 상호작용에 따라 그 양자 과정 자체를 제어할 수 있습니다. 우리는 프로그램된 음향광학 주파수 필터(Dazzler)이용하여 초고속 레이져를 재단하여 양자 시스템을 제어하고 있습니다. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
<big><big>'''Results</big></big><br> | <big><big>'''Results</big></big><br> | ||
| Line 67: | Line 60: | ||
==테라헤르츠파 제어== | ==테라헤르츠파 제어== | ||
| − | + | [[Image:whatisterahertz.jpg|center|400px]] | |
| + | |||
| + | 흔히 테라헤르츠 파라고 불리는 0.1 ~ 10 THz의 주파수 대역의 전자기파의 입니다. 특히 통신, 물체 특성 측정, 바이오 메디컬 이미징, 분자에서의 정확한 분광 측정등 여러 분야에서 테라헤르츠 파의 응용이 기대 되기 때문에 그 중요도가 점점 증가되고 있습니다. 이중에서 테라헤르츠 시분해 분광 기술(THz-TDS)은 테라헤르츠 기술 응용의 한축을 차지하는 기술로서 테라헤르츠 대역대의 물체의 광학적 성질 측정 및 이미징에 있어서 그 응용이 기대되고 있습니다. 저희 랩에서는 특히 이러한 테라헤르츠 시분해 분광 기술을 제어하는 적극 소자를 개발하고 있습니다. | ||
| + | |||
<big><big>'''Results</big></big><br> | <big><big>'''Results</big></big><br> | ||
| Line 91: | Line 87: | ||
==초고속 제어 및 측정== | ==초고속 제어 및 측정== | ||
| − | [[Image:pp01.png|center| | + | [[Image:pp01.png|center|400px]] |
| − | |||
| − | + | 시간 분해 펌프-프로브 실험은 전자와 포논 그리고 스핀등의 역학적 특성 공부에 유용한 방법입니다. 이 실험 방법은 다음과 같습니다. 먼저 '펌프 빔' 이라고 불리는 강한 레이져 펄스를 보고자하는 샘플에 조사하여 샘플을 비평형 상태로 만듭니다. 샘플은 그후 다시 새로운 평형 상태로 돌아가게 됩니다. 이러한 과정은 '프로브 빔' 이라고 불리는 샘플에 조사되는 충분히 약한 레이져 펄스를 통해 측정되어 집니다. 즉 프로브 빔을 통해 펌프빔에 의해 바뀌는 샘플의 광학적 특성의 변화를 보는 것 입니다. | |
| + | 우리는 이렇게 초고속 시간 분해능으로 제어되는 실험을 통해 전자가 상호 연관된 물질 특히 rare-earth manganites 물질의 전자와 포논 그리고 스핀등의 초고속 동역학을 연구하고 있습니다. | ||
<big><big>'''Results</big></big><br> | <big><big>'''Results</big></big><br> | ||
Latest revision as of 07:29, 30 August 2010
개요
본 실험실은, 초고속 레이저 기술을 이용하여, 다양한 양자계의 결맞음성, 중첩성, 및 얽힌성을 생성, 변조, 및 측정하는 연구를 수행합니다. 이를 위하여, 알칼리 원자, 분자, 반도체 나노 구조 및 고체 양자계 등의 양자 상태를 분광, 제어, 및 이미징하는 다양한 초고속 광학 기술을 개발하고 있으며, 특히, 펨토초 광학 및 테라헤르쯔파를 이용한 알고리듬형 양자 상태의 제어, 즉 초고속 양자 컴퓨팅의 구현을 목표로 하고 있습니다.
(1) 양자 결맞음 분광학 : 최근 개발된 결맞음 제어 분광 기술을 통하여, 빛과 다양한 양자계의 상호작용을, 고전적인 한계 이상의 양자 효율로, 양자역학적으로 제어합니다. 2준위 원자 및, 3준위 사다리형 및 V형 원자의 해석적 양자 제어법을 개발하였으며, 다차원 푸리어 분광 양자 제어 기술을 개발을 통하여 양자 논리 소자를 구현하고 있습니다.
(2) THz 광학 기술 : THz파는 피코초의 짧은 결맞음성을 갖는 양자계를 전기적으로 제어할수 있는 21세기의 새로운 광원이며, 광원 개발, 기초 광학 현상 및 물질의 반응 규명 등 다양한 연구분야가 활발히 연구되고 있습니다. 본 실험실은, 극한적 THz파 물리 현상, 예를 들어, THz 나노분광 및 비선형 분광법을 연구하고 있으며, 궁극적으로는 THz파 양자 제어를 목표로 합니다.
(3) 새로운 양자계 : 차세대의 양자 제어 분광 대상으로, 다양한 새로운 양자계에 대한 탐사적 연구를 진행하고 있으며, 분자, 반도체 나노 구조 및 강상전자계의 초고속 현상을 연구합니다.
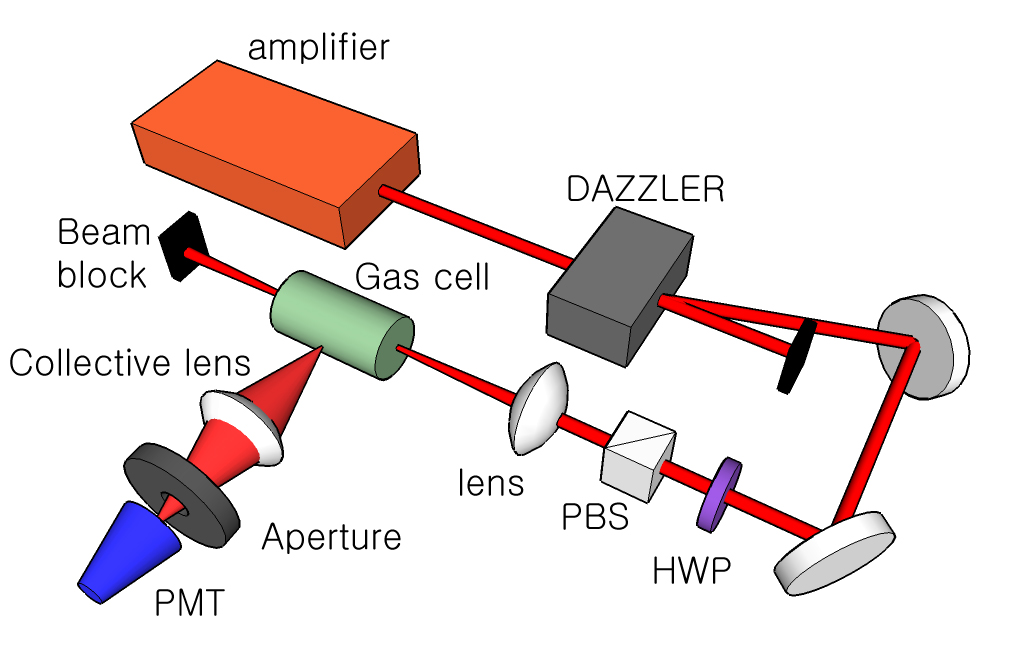
양자 제어
초고속 레이져 펄스는 재단됨에 따라 양자 시스템에 다른 영향을 주며 따라서 빛과 물질의 상호작용에 따라 그 양자 과정 자체를 제어할 수 있습니다. 우리는 프로그램된 음향광학 주파수 필터(Dazzler)이용하여 초고속 레이져를 재단하여 양자 시스템을 제어하고 있습니다.
Results
Strong-field two-photon absorption in atomic cesium: an analytical control approach
We have considered an analytical control of two-photon absorption
process of atoms in the strong-field interaction regime. The experiment
was performed on gaseous cesium atoms strongly interacting with a
shaped laser-pulse from a femtosecond laser amplifier and a programmable
pulse-shaper. When this shaped laser-pulse transfers the atomic population
from the 6s ground state to the 8s excited state, we have found that both
positively- and negatively-chirped laser pulses, compared with a Gaussian
pulse, enhance this excitation in the strong-field regime of laser-atom
interaction. This unusual phenomena is explained because the temporal
shape of the laser intensity compensates the effect of dynamic Stark shift for
the two-photon resonant condition to be optimally maintained. We provide
analytic calculations using the strong-field phase matching, which show
good agreement with the experiment.
27 April 2009 / Vol. 17, No. 9 / OPTICS EXPRESS 7648
Strong-Field two-photon transition by phase shaping
We demonstrate the ultrafast coherent control of a non-linear two-photon absorption in a dy-
namically shifted energy level structure. We use a spectro-temporal laser pulse shaping that is
programmed to preserve the resonant absorption condition during the intense laser field interaction.
Experiments carried out in the strong-field regime of two-photon absorption in the ground state
of atomic Cesium reveal that the analytically obtained o®set and curvature of a laser spectrum
compensate the effect of both static and dynamic energy shifts of the given light-atom interaction.
PRA accepted Tuesday Jul 20, 2010
Coherent Control in 2D-FTES
We demonstrate the advantage of applying coherent control technique to 2D-FTES spectroscopy. By shaping individual pulses used in 2D-FTES on atomic model system, we selectively turn on and off specific couplings. This advanced 2D-FTES technique may be useful for probing time-dependent coupling paths among multilevel electronic energy states in complex systems
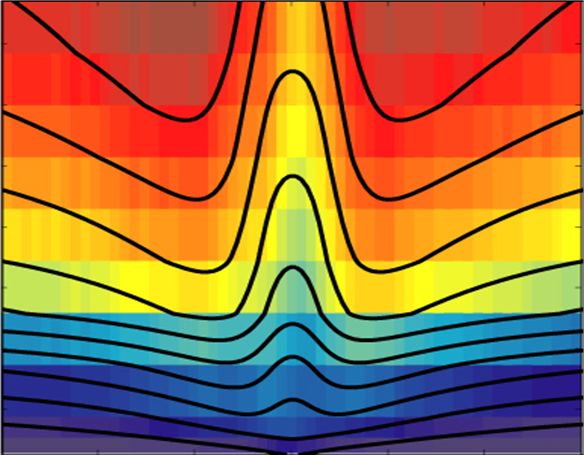
테라헤르츠파 제어
흔히 테라헤르츠 파라고 불리는 0.1 ~ 10 THz의 주파수 대역의 전자기파의 입니다. 특히 통신, 물체 특성 측정, 바이오 메디컬 이미징, 분자에서의 정확한 분광 측정등 여러 분야에서 테라헤르츠 파의 응용이 기대 되기 때문에 그 중요도가 점점 증가되고 있습니다. 이중에서 테라헤르츠 시분해 분광 기술(THz-TDS)은 테라헤르츠 기술 응용의 한축을 차지하는 기술로서 테라헤르츠 대역대의 물체의 광학적 성질 측정 및 이미징에 있어서 그 응용이 기대되고 있습니다. 저희 랩에서는 특히 이러한 테라헤르츠 시분해 분광 기술을 제어하는 적극 소자를 개발하고 있습니다.
Results
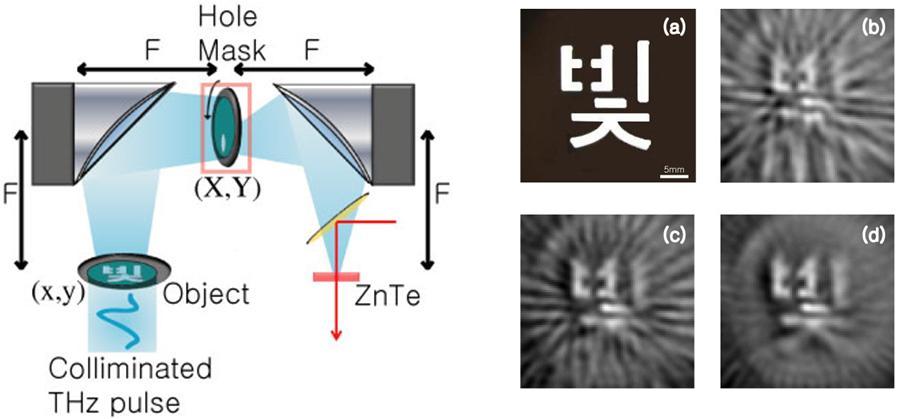
THz coherent optical computer
Single point terahertz imagery of 2D objects is demonstrated by exploiting the broadband nature of ultrafast terahertz wave in a coherent optical computing setup. In the devised imagery, a collimated terahertz beam is illuminated on an object and the scattered fields are measured through a spatial mask at the Fourier plane in a 4-f terahertz time-domain spectroscope. This arrangement allows conversion of radial spatial frequencies of the object to the temporal spectrum of the pulse. Hence, a 2D image stored in the terahertz waveforms can be readily obtained.
Optics Letters, Vol. 35, Issue 4, pp. 508-510 (2010)
single-pixel coherent diffraction imaging
We demonstrate single-pixel coherent diffraction imaging, whereby broadband terahertz (THz) waveforms passed through a slated phase retarder (SPR), diffracted from an object, were measured by a THz detector located in the far field. For 1D imaging, the fixed-location single-pixel broadband detector simultaneously measured all the spatial frequency components of the object because the frequency components of the source maintain a one-to-one correspondence with the object's spatial frequency. For 2D imaging, the angular position of the SPR enabled the diffracted THz wave to carry an angular projection image of the object. Thirty waveforms measured at different SPR orientations successfully reconstructed complex 2D images.
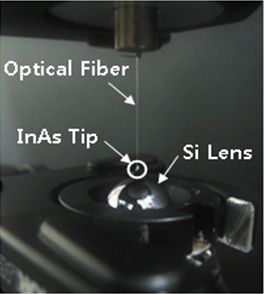
Terahertz Waves Emitted from an Optical Fiber
We report a simple method of creating terahertz waves by applying the photo-Dember effect in a (100)-oriented InAs film coated onto the 45-degree wedged-end facet of an optical fiber. The terahertz waves are generated by infrared pulses guided through the optical fiber which is nearly in contact with a sample and then measured by a conventional photo-conductive antenna detector. Using this alignment-free terahertz source, we performed proof-of-principle experiments of terahertz timedomain spectroscopy and near-field terahertz microscopy. We obtained a bandwidth of 2 THz and 180-mm spatial resolution. Using this method, the THz imaging resolution is expected to be reduced to the size of the optical fiber core. Applications of this device can be extended to sub-wavelength terahertz spectroscopic imaging, miniaturized terahertz system design, and remote sensing.
21 June 2010 / Vol. 18, No. 13 / OPTICS EXPRESS 13693
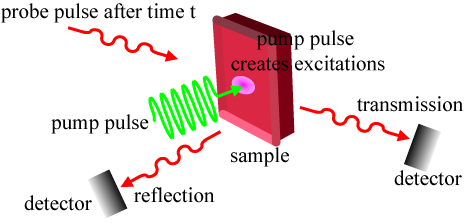
초고속 제어 및 측정
시간 분해 펌프-프로브 실험은 전자와 포논 그리고 스핀등의 역학적 특성 공부에 유용한 방법입니다. 이 실험 방법은 다음과 같습니다. 먼저 '펌프 빔' 이라고 불리는 강한 레이져 펄스를 보고자하는 샘플에 조사하여 샘플을 비평형 상태로 만듭니다. 샘플은 그후 다시 새로운 평형 상태로 돌아가게 됩니다. 이러한 과정은 '프로브 빔' 이라고 불리는 샘플에 조사되는 충분히 약한 레이져 펄스를 통해 측정되어 집니다. 즉 프로브 빔을 통해 펌프빔에 의해 바뀌는 샘플의 광학적 특성의 변화를 보는 것 입니다.
우리는 이렇게 초고속 시간 분해능으로 제어되는 실험을 통해 전자가 상호 연관된 물질 특히 rare-earth manganites 물질의 전자와 포논 그리고 스핀등의 초고속 동역학을 연구하고 있습니다.
Results
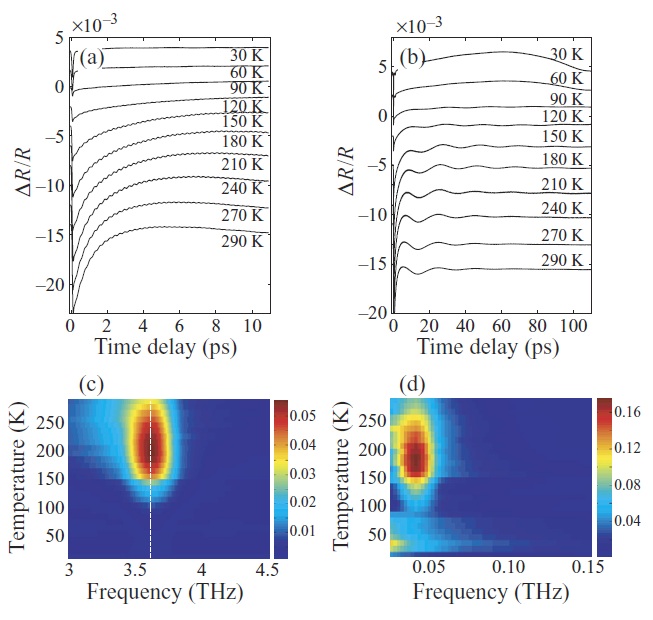
Ultrafast IR spectroscopic study of coherent phonons and dynamic spin–lattice coupling in multiferroic LuMnO3
The concurrent existence of ferroelectricity and magnetism within
a single crystalline system characterizes the multiferroic materials discovered
in recent years. To understand and develop the multiferroic phenomenon, we
need to investigate the unusual coupling between spin and lattice degrees of
freedom. Spins in multiferroics are expected to be elastically coupled to phonons.
Therefore, the time-dependent study can be a crucial factor in understanding
the coupled dynamics. Here, we report the observations of strong dynamic
spin–lattice coupling in multiferroic LuMnO3. A coherent optical phonon of
3.6 THz and its temperature dependence is measured for the first time from our
femtosecond IR pump and probe spectroscopy. Also, we observed a coherent
acoustic phonon of 47 GHz similar to a previous report (Lim et al 2003 Appl.
Phys. Lett. 83 4800). Temperature-dependent measurements show that both
optical and acoustic phonons become significantly underdamped as temperature decreases to TN, and they disappear below TN. These observations reveal that
phonons are coupled to spins by magneto-elastic coupling, and the disappearance
of phonon modes at TN is consistent with the isostructural coupling scheme
suggested by Lee et al (2008 Nature 451 805).
New Journal of Physics 12 (2010) 023017
Ultrafast near-infrared spectroscopic study of coherent phonons in the phase-separated manganite La1/4Pr3/8Ca3/8MnO3
We report the generation of coherent optical and acoustic phonons in mixed valent manganite
La1/4Pr3/8Ca3/8MnO3 using femtosecond infrared pump-probe spectroscopy. Temperature-dependent measurements
of the time-resolved optical reflectance, obtained over a range of 5–300 K, revealed that the energy of
the photoexcited electrons dissipated during relaxation to acoustic phonons, in the high-temperature paramagnetic
phase, and to optical phonons, in the low-temperature charge-ordering phase. Analysis of the temperaturedependent
behavior reveals that the modal amplitudes of the coherent phonons appear strongly correlated with
the charge-ordering phase.
Phys. Rev. B 81, 214416 (2010)
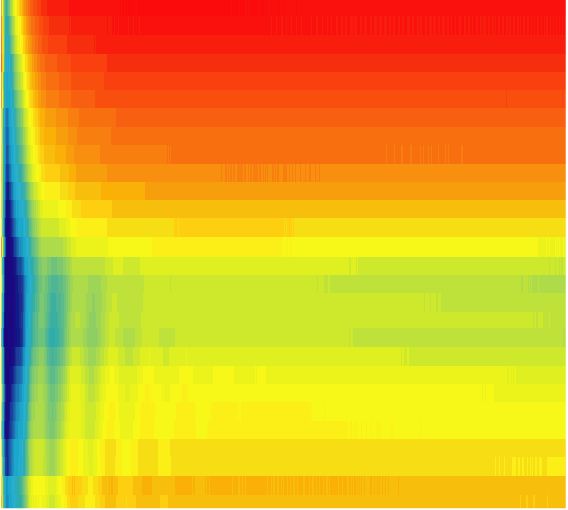
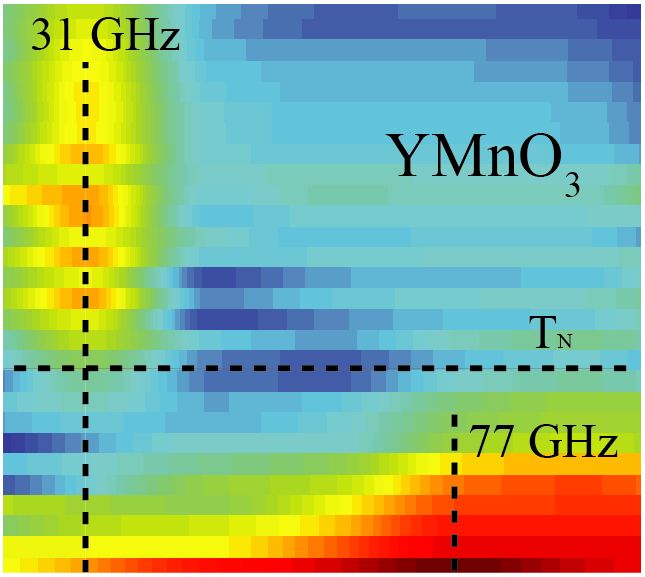
Strong spin-lattice coupling in multiferroic hexagonal manganite YMnO3 probed by ultrafast optical spectroscopy
We report the observation of spin-lattice coupling in multiferroic YMnO3 by femtosecond near-infrared pump and probe spectroscopy. A coherent 31~GHz acoustic phonon was detected above the magnetic ordering temperature, and a higher frequency coherent mode was observed in the anti-ferromagnetic phase. This temperature-dependent measurement demonstrates that the acoustic phonon excitation is coupled to spin ordering.